

With Windows PowerShell 2.0 that situation has changed somewhat.
#Windows command line ldap query tool pro
#Best free ldap query tool pro#īy using the techniques seen here, an IT Pro now has a supportable command line solution to the problem of performing Active Directory queries.
There are a couple of options available to you for querying Active Directory from the Windows PowerShell prompt. The type accelerator is a shortcut to the class. All the type accelerator does is save you a bit of typing. You still have to give it the appropriate constructor to create an instance of the class. If you did not use the you would need to use the New-Object cmdlet to create the object. You can put the New-Object command inside smooth parentheses to force the creation of the object first, and then call the FindAll method from the DirectorySearcher object. LDAP://CN=VistaAdmin,OU=Students,DC=nwtraders,DC=com LDAP://CN=VISTA,CN=Computers,DC=nwtraders,DC=com LDAP://CN=krbtgt,CN=Users,DC=nwtraders,DC=com LDAP://CN=BERLIN,OU=Domain Controllers,DC=nwtraders,DC=com LDAP://CN=Guest,CN=Users,DC=nwtraders,DC=com LDAP://CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=nwtraders,DC=com PS C:\> (New-Object DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher “ObjectClass=user”).Find The resulting collection of DirectoryEntry objects is pipelined to the Select-Object cmdlet where the Path property is returned.
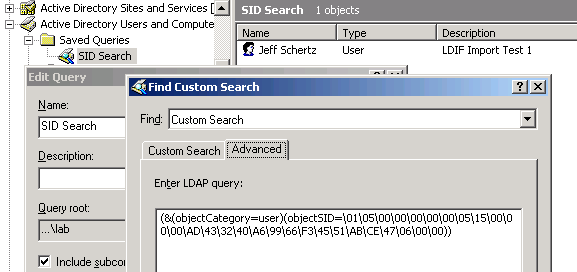
To use the type accelerator, you still need to supply it with an appropriate constructor that in many cases will be the search filter expressed in LDAP Search Filter Syntax. LDAP Search Filter Syntax is defined in RFC 2254 and is represented by Unicode strings. (&(ObjectCategory=OrganizationalUnit)(Name=*Berlin*)(!L=*))Īll organizational units with a name that contains Berlin, but do not have any location specified (&(ObjectCategory=OrganizationalUnit)(Name=*Berlin*)(!L=Berlin))Īll Organizational Units with a name that contains Berlin, but do not have a location of Berlin (&(ObjectCategory=OrganizationalUnit)(Name=*Berlin*))Īll Organizational Units with a name that contains Berlin (&(L=berlin)(ObjectCategory=OrganizationalUnit))Īll Organizational Units with the location of Berlin (&(ObjectCategory=User)(ObjectClass=Person))Īll objects with a name that contains Berlin Some examples of using the LDAP Search Filter Syntax are seen in Table 1.Īll user objects as well as all computer objects The search filters enable you to specify search criteria in an efficient and effective manner. (&(ObjectCategory=OrganizationalUnit)(|(L=Berlin)(L=Charlotte)))Īll Organizational Units with a location of either Berlin or CharlotteĪs seen in the examples in Table 1 there are two ways in which the search filter can be specified. The first method is a straight forward assignment filter. PS C:\> (”Name=Charlotte”).FindAll() | Select Path The attribute, the operator, and the value make up the filter. The second way to use the LDAP Search Filter is to combine multiple filters. You will have the operator, then filter A followed by filter B. You can combine multiple filters and operators as seen in the syntax examples in Table 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
